Explaining Digital Video Formats
In this article, i am explaining the video formats, codecs and containers
by Rahul Vishwakarma
This article is taken from Explaining Computers youtube video. (Credit to Explaining Computers)
Digital video is combination of codecs and containers.
Codec : Coder-decorder algorithm used to encode the video.
| Comman Codecs | Comman Containers |
|---|---|
| H.264/AVC | MP4 |
| H.265/HEVC | AVI |
| H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2 | MOV |
| M-JPEG | MXF |
| ProRes | 3DP & 3G2 |
| _ | MTS, M2TS & TS |

Intraframe vs Interframe compression
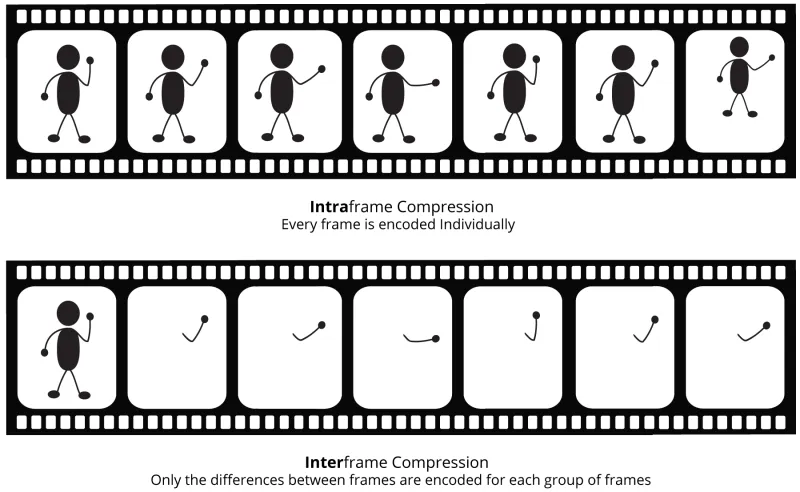
Intraframe compression (also called spatial compression) reduces the size of each individual frame independently by reducing redundant information within the frame, similar to how JPEG compression works for still images. This compression technique reduces file size while maintaining high image quality.
Interframe compression (also called temporal compression) reduces file size across multiple frames by creating a starting point and then only saving the changes in subsequent frames. By using this compression technique, only the changes between frames are saved resulting in drastically reduced file sizes. (Read More)
# Common Intraframe Codecs
# Common Intraframe Codecs
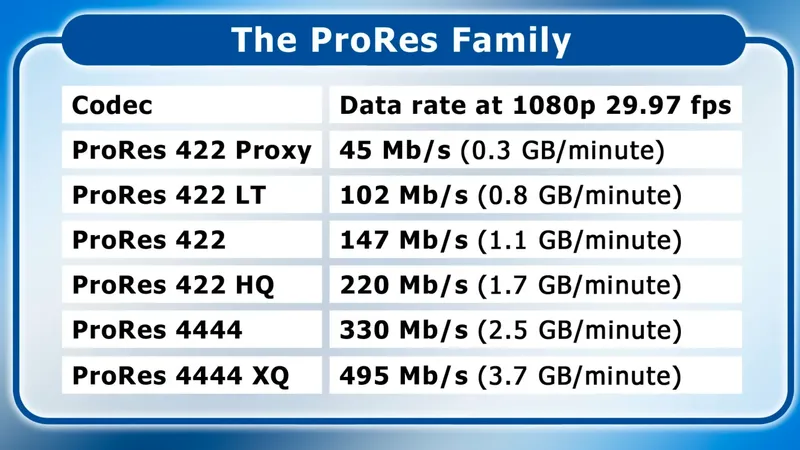
# DNxHD and DNxHD
# H.264 / AVC - advanced video coding
• Defined by Motion Picture Experts Group
(MPEG) in Part 10 of the MPEG-4 standard.
• Mostly, H.264 is an interframe codec that
produces relatively small video files.
• But there is an intraframe implementation,
usually described as I-frame H.264.
# H.265 / HEVC - high efficiency video coding
• Defined by MPEG in Part 2 of MPEG-H.
• Produces interframe video with the same
quality as interframe H.264, but with
roughly half the data rate and file size.
• H.265 = HEVC = ‘high efficiency video
coding’.
• Defined by MPEG in Part 2 of MPEG-H.
• Produces interframe video with the same
quality as interframe H.264, but with
roughly half the data rate and file size.
• But requires more processing than H.264.
# H.262 / MPEG -2
• H.262 defined by MPEG in Part 2 of their
MPEG-2 standard
• Not as efficient as H.264 or H.265, so
produces much larger video files.
• Still widely used for SD digital television
broadcasts and DVDs.
# Common Containers
• MP4, AVI and MOV.
• MP4 defined by MPEG in MPEG-4 Part 14.
• AVI developed by Microsoft and stands
for ‘audio video interleave’.
• MOV created by Apple and is short for
‘movie’.
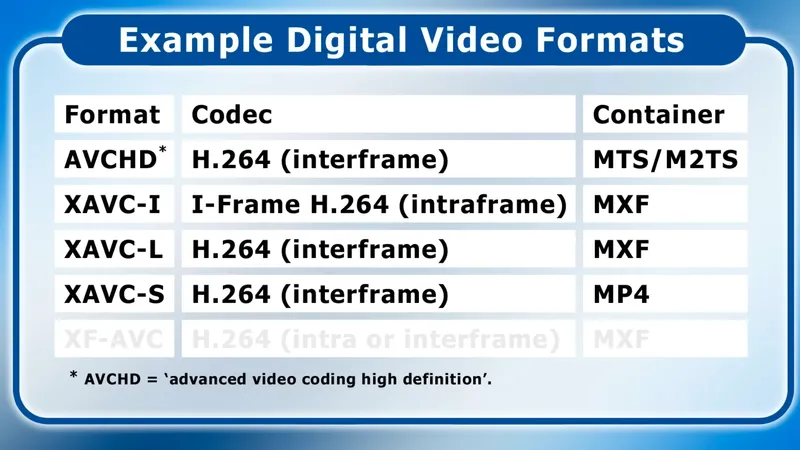
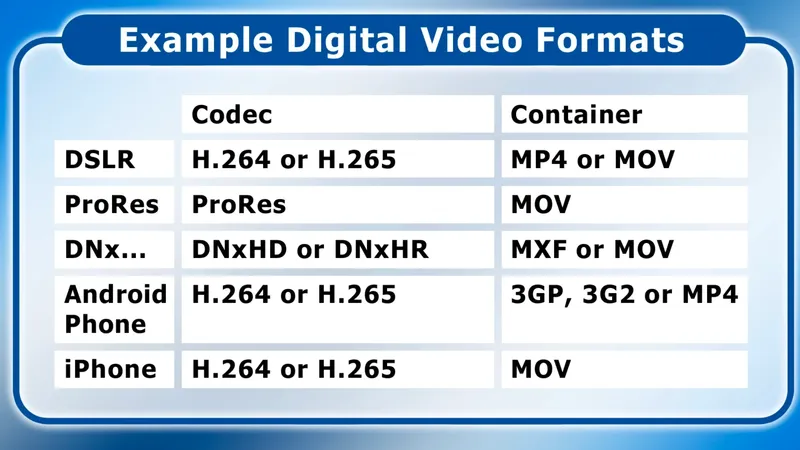
Thank You!!!